Indonesia’s tax system continues to play a pivotal role in supporting national development and achieving fiscal sustainability. However, enhancing tax revenue remains a significant challenge for the government, as annual targets consistently rise amidst various obstacles.
As of 31 October 2024, Indonesia tax revenue reached IDR 1,517.5 trillion, approximately 76.3% of the State Budget (APBN) target of IDR 1,988.88 trillion. While this figure approaches the target, it represents a 0.4% contraction compared to the same period in 2023, when tax revenue was IDR 1,523.9 trillion.
Several factors, including declining palm oil and coal prices, have contributed to slower tax revenue growth. These commodities are critical sources of tax income, and the downturn has led Minister of Finance Sri Mulyani Indrawati to acknowledge the difficulties faced in 2024. Addressing the House of Representatives (DPR) Commission XI, she described 2024 as a challenging year for tax collection.
Tax Return Performance in 2024
Despite these challenges, there are signs of improvement in certain tax components. Value Added Tax (VAT) and Luxury Goods Sales Tax (PPnBM) showed a growth of 7.87%, while Property Tax (PBB) rose by 12.81%. However, Income Tax (PPh) from the oil and gas sector continued to contract due to declining crude oil production.
You may also want to read: Indonesia Introduces New PNBP Regulations for Immigration Services
Looking ahead, the urgency of tax reform is clear. The 2025 tax revenue target is set at IDR 2,189.3 trillion, an increase of around IDR 200 trillion from the 2024 target. Considering the slower revenue growth in 2024, achieving this ambitious goal will require innovative strategies and significant structural changes.
Introducing Coretax in January 2025
To address these challenges, the government has initiated various reforms, with the Core Tax Administration System (CTAS), or Coretax, being a cornerstone initiative. This system is designed to enhance efficiency, transparency, and accountability in tax administration. By automating administrative processes and employing risk-based data analysis, Coretax aims to improve taxpayer compliance and streamline operations.
Minister Sri Mulyani projects that Coretax could increase Indonesia’s tax-to-GDP ratio by 1.5%, raising it from the current 10.02% to 11.5%. Officials rescheduled Coretax’s implementation from mid-2024 to early 2025 to allow for further refinement of its features and services.
Simplifying Tax Regulations with PMK No. 81/2024
In preparation for Coretax, the Ministry of Finance issued Regulation No. 81/2024 (PMK No. 81/2024), which overhauls existing tax regulations. This reform streamlines and consolidates 42 previous tax rules to create a more straightforward and efficient tax system.
One significant change introduced by this regulation is the standardisation of tax payment and filing deadlines. While deadlines are now unified for certain tax types, variations remain for others. For example:
- Taxes such as PPh Article 21, Article 22, and VAT must be paid by the 15th of the following month.
- VAT on luxury goods and customs-related taxes are due one day after collection by the Directorate General of Customs and Excise (DJBC).
- Specific deadlines apply for Income Tax (PPh) on founder shares and VAT/PPnBM collected by third parties.
These adjustments aim to simplify compliance for taxpayers while improving administrative efficiency for the Directorate General of Taxes (DJP).
Enhancing Taxpayer Engagement
As part of the Coretax launch, the DJP is actively educating the public to ensure a smooth transition. This outreach includes workshops, informational campaigns, and online resources to help taxpayers understand and utilise the new system effectively.
Additionally, Coretax introduces centralised management of taxpayer accounts using the taxpayer identification number (NPWP). This change will standardise the administration of taxes such as Property Tax (PBB) for the 2025 fiscal year and beyond.
Opportunities for Expatriates and Investors
For expatriates and business investors, understanding Indonesia’s evolving tax landscape is crucial. The introduction of Coretax and associated reforms offers several advantages:
- Automated processes reduce the risk of errors and corruption, ensuring fair treatment for all taxpayers.
- Simplified regulations and unified deadlines make it easier for businesses to meet their tax obligations.
- Faster processing times for tax payments and refunds improve cash flow management for businesses.
However, these changes also come with new responsibilities. Businesses must adapt to updated reporting requirements, while expatriates should seek professional advice to navigate Indonesia’s complex tax environment.
How to access Indonesian Coretax System?
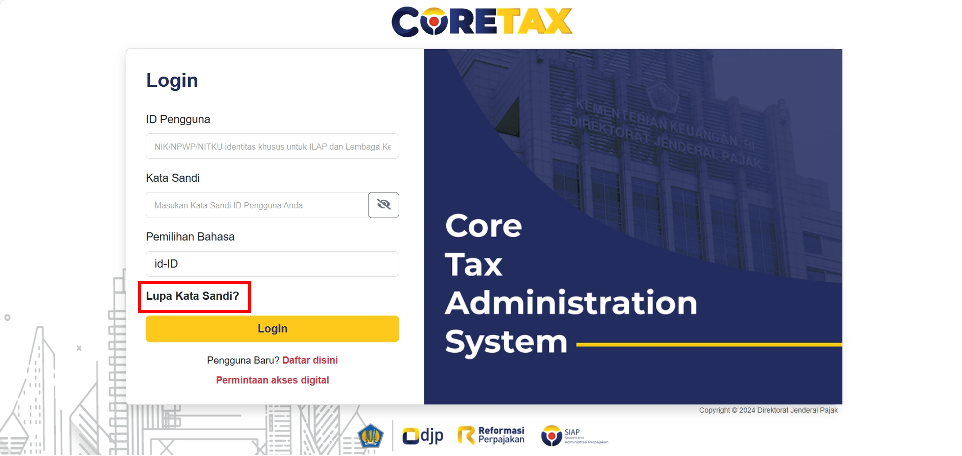
Here’s how to access the Coretax system:
- Enter your user ID, which is either your National Identity Number (NIK) or Taxpayer Identification Number (NPWP).
- Enter the password for your DJPOnline account.
- Enter the captcha code displayed on the screen.
- Click login.
- You will be prompted to reset your password.
- Choose where you would like to receive the password reset confirmation, either by email or SMS.
- Open the link from the email or SMS and complete the process of creating a new password and passphrase for your electronic signature.
- Once completed, you can access the Coretax service.
Taxpayers can access Coretax through pajak.go.id website. The Directorate General of Taxation (DGT) of the Ministry of Finance previously conducted a pre-implementation of Coretax from 24 to 31 December 2024.
The DGT recommends verifying taxpayer data before accessing Coretax. This primarily refers to your email address and mobile phone number.
If you already have a DJPOnline account, you can log in to the Coretax system for the first time and start using it from 1 January 2025.
For taxpayers who already have a Taxpayer Identification Number (NPWP) but have never used the DJP Online service, you can still access Coretax. Simply submit a request for digital service access through the ‘Digital Access Request’ menu.
Meanwhile, those who do not yet have an NPWP and wish to register as taxpayers can also do so directly through Coretax. Registration can be done via the registration menu on the website.
Key Considerations for 2025
Several aspects of the tax system remain under review, including exemptions for specific taxpayer categories from filing annual tax returns (SPT). These criteria will be detailed in forthcoming regulations by the DJP. Additionally, provisions for tax payments in foreign currencies, particularly US dollars, are being refined to accommodate international business operations.
How to Navigate Indonesia’s Tax Regulation Updates in 2025
Indonesia’s tax reform efforts underscore the government’s commitment to creating a robust and sustainable fiscal framework. Despite global economic challenges and fluctuating commodity prices, the implementation of Coretax represents a significant step forward in modernising the country’s tax system.
By fostering a more efficient and transparent tax environment, these reforms aim to enhance compliance, boost revenue, and support Indonesia’s economic growth.
For expatriates, investors, and local businesses, staying informed and proactive will be essential to navigating this dynamic landscape and leveraging the opportunities it presents.
Have more questions regarding tax in Indonesia?
If you need further guidance or professional assistance with tax matters in Indonesia, Lets Move Indonesia’s team of experts is here to help. Contact us today to learn how we can support your business and investment goals in 2025 and beyond.