Tax season in Indonesia has arrived once again, signalling individuals and corporates in Indonesia to report the past year’s financial activity. With the deadline for filing just around the corner, it’s crucial to stay informed on the latest tax laws and regulations governing your obligations as a taxpayer.
Regardless of your employment status or type of income, knowing the ins and outs of the tax system is the key to maximising your returns and minimising potential headaches down the line. In this article, Lets Move Indonesia will discuss the essential details of annual tax returns in Indonesia, providing you with a comprehensive guide on how to prepare and file for the year ahead.
What is Annual Tax Reporting and why is it important?
Annual Tax Reporting or an Annual Tax Return in Indonesia a document that taxpayers must submit to the Indonesian tax authority, typically by the end of March every year. The tax return contains information on the taxpayer’s income, deductions, and tax liability for the previous year.
It is important to stay compliant by submitting the Annual Tax Return on time. It serves as a way for taxpayers to claim deductions and credits they are entitled to, which can help reduce their tax liability.
Furthermore, a failure to file an accurate and timely Annual Tax Return is crucial for individuals and businesses in Indonesia and can result in penalties and fines. Additionally, a clean tax record can help individuals and businesses avoid legal troubles and maintain good standing with the tax authority.
Who should report tax in Indonesia?
Individuals and businesses who meet certain criteria are required to report and pay taxes to the tax authority. The specific tax obligations and reporting requirements depend on the type and size of the business, as well as the individual’s income level.
Individual taxpayers in Indonesia are generally required to file tax returns and pay taxes if their annual income exceeds a certain threshold. As of 2021, this threshold is set at IDR 54 million per year.
Businesses in Indonesia are required to register with the tax authority and obtain a tax identification number (NPWP) if they meet certain criteria. This includes businesses with an annual turnover exceeding IDR 4.8 billion, as well as certain types of businesses such as restaurants, hotels, and entertainment venues.
Annual Tax Return Regulation for Expats
Expatriates working in Indonesia are generally subject to the same tax reporting requirements as Indonesian citizens. This means that if an expatriate’s income exceeds the threshold for tax liability, they must file an Annual Tax Return with the tax authority.
- Expatriates who work in Indonesia are typically classified as resident taxpayers if they spend more than 183 days in the country during a calendar year. In this case, they are subject to the same tax rates and deductions as Indonesian citizens.
- Expatriates who work in Indonesia but are classified as non-resident taxpayers are generally subject to a flat tax rate of 20% on their income earned in Indonesia. Non-resident taxpayers are not eligible for many of the same deductions and tax breaks as resident taxpayers.
In addition to reporting their income and tax liability, expatriates in Indonesia may also need to report certain assets and transactions to the tax authority. For example, expatriates who own property or other assets in Indonesia may be required to report these assets and pay additional taxes on them.
How many tax form categories and how to know which one should you report?
There are several types of Annual Tax Return forms, each designed for different types of taxpayers. The specific form that a taxpayer needs to use depends on their individual circumstances and the type of income they received during the tax year. Here are some of the main types of Annual Tax Return forms in Indonesia:
Tax reporting forms for Individual tax returns
- Form 1770: This form is used by individual taxpayers who earn income from employment, business, or investments. It includes sections for reporting income, deductions, tax credits, and other relevant information.
- Form 1770S: This form is a simplified version of Form 1770 and is used by individual taxpayers who earn income only from employment and have no other sources of income or deductions.
- Form 1770SS: This form is used by individual taxpayers who earn income from self-employment or freelance work. It includes sections for reporting income, expenses, and tax credits.
- Form 1721-A1: This form is used by employers to report the income, taxes withheld, and other information for their employees. It includes sections for reporting salary, bonuses, benefits, and other forms of compensation.
Tax forms for corporate tax return
- Corporate Income Tax Return Form (SPT Tahunan PPh Badan) – This form is used to report the annual corporate income tax.
- Land and Building Tax Return Form (SSPD PBB) – This form is used to report the land and building tax for corporate-owned properties.
- Final Income Tax Return Form (SPT PPh Final) – This form is used to report the final income tax for certain types of income, such as income from royalties, prizes, and winnings.
It’s important to note that the specific forms used may vary depending on the nature of the business and the taxes being reported.
In addition to these main forms, there are also various supplementary forms and schedules that taxpayers may need to complete depending on their circumstances. Consulting with qualified tax professionals is important to ensure that all required forms are completed accurately and filed on time.
How to submit The Annual Tax Return?
Reporting your annual tax in Indonesia should be done by following these steps:
- Determine your tax status: Before you can report your annual tax, you need to determine your tax status. If you are an employee, you will have tax deducted from your salary by your employer. If you are a business owner, you will need to calculate your taxable income and report it to the tax office.
- Obtain a Tax Identification Number (NPWP): If you don’t have an NPWP, you will need to obtain one from the tax office. This unique identification number is required for all taxpayers in Indonesia.
- Collect all relevant information: Gather all information related to your income, deductions, and tax payments made during the year.
- Determine the correct tax form to use: There are several tax forms available in Indonesia, depending on your type of income and other factors. Make sure you use the correct form that corresponds to your income and tax status.
- Complete the tax form: Fill out the tax form accurately and completely. Make sure to double-check all calculations and information to avoid errors.
- Submit the tax return: Submit the completed tax form to the tax office by the deadline. The deadline for filing tax returns in Indonesia is typically March 31st of the following year.
- Pay any taxes owed: If you owe taxes, you need to pay them by the deadline. The deadline for paying taxes in Indonesia is typically April 30th of the following year.
Keep records: It’s important to keep copies of your tax returns and any supporting documents in case of an audit or future inquiries.
When is the deadline to submit your tax reporting in Indonesia?
Individual taxpayer
The deadline to report your tax obligation in Indonesia is typically March 31st of the following year. This means that if you earned income during the calendar year, you must report your tax obligation to the tax office no later than March 31st of the following year.
Corporate taxpayer
As for corporate, the deadline for reporting corporate tax returns depends on the type of entity and the fiscal year. Generally, corporate taxpayers are required to file their tax returns by the last day of the fourth month following the end of their fiscal year.
For example, if a company’s fiscal year ends on December 31, the corporate tax return is due on April 30 of the following year. However, if the taxpayer’s fiscal year ends on a date other than December 31, the tax return filing deadline is the last day of the fourth month following the end of the fiscal year.
Is the Annual Tax Return the same as Annual Tax Reporting?
The terms “Annual Tax Return” and “Annual Tax Reporting” generally refer to the same thing. Both terms address the process of reporting your annual income and tax obligations to the tax office.
Why report the Annual Tax Return from Lets Move Indonesia?
Additionally, reporting your tax return accurately can help you avoid any issues or inquiries from the tax office. It can also help you to better understand your tax obligations and potential deductions that you may be eligible for.
Working with a reputable tax service provider like Lets Move Indonesia will be a huge help, especially if you are unfamiliar with the tax reporting process in Indonesia. We guide what forms you have to file for your tax subject; what documents to include, and can help ensure that your tax return is filed accurately and on time.
Found this article helpful? Check out some of other interesting articles below
Tax in Indonesia: Your Common Questions Answered
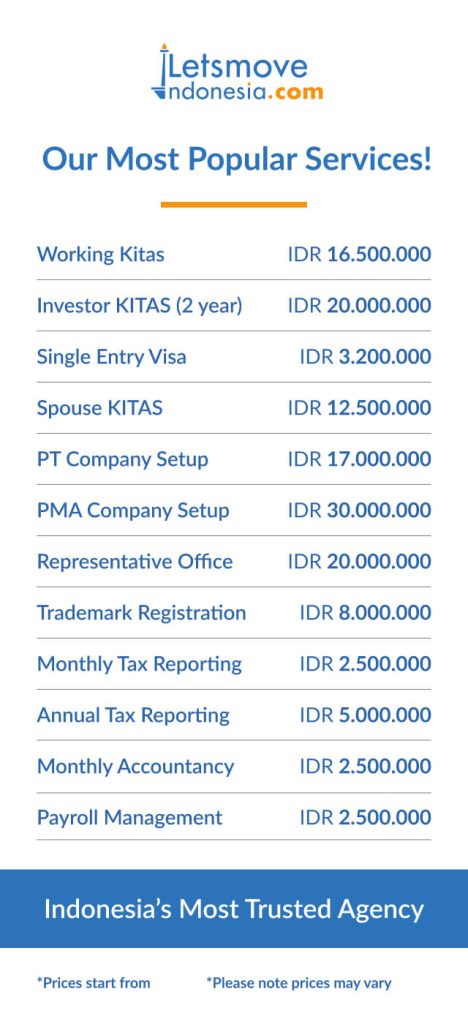
The LetsMoveIndonesia Tax & Accountancy Packages
LetsMoveIndonesia Wins The Most Trusted Visa & Legal Agency Awards
MEBV Is Now Available For All Immigration Points in Indonesia