Indonesia welcomed the inauguration of its membership in BRICS organisation after being announced by the 2025 Chair of BRICS, Brazil on Monday, (6/1/2025).
Through the official statement, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs confirmed that the membership in BRICS represents a strategic step to strengthen democratic collaboration with other developing countries under the framework of inclusivity, equality, mutual respect and sustainable development.
Indonesia’s Minister of Foreign Affairs, Sugiono, emphasised that the Republic of Indonesia is welcoming the addition to mark Indonesia’s increasing active role in global issues and commitment to strengthen multilateral cooperation. This goes in line with Indonesia’s participation in various other global forums, such as G20, APEC, IPEF, MIKTA, and CPTPP, as well as the accession process to become a member of the OECD.
In this article, we will discuss BRICS, its objectives and the impacts on Indonesia’s economic and tourism development.
What is BRICS?
According to the Council on Foreign Relations, BRICS stands as an intergovernmental organisation of countries that aims to promote peace, security, and cooperation. The acronym stands for the initials of the first five member countries: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
Established in 2009, The BRICS group has become a major political force in the last two decades. This organisation was founded on the premise that international institutions were overly dominated by Western powers and had ceased to serve developing countries. The bloc has sought to coordinate its members’ economic and diplomatic policies, found new financial institutions, and reduce dependence on the U.S. dollar.
The BRICS currently consists of 9 member countries, with an accumulated economy of 26% of global GDP and representing 45% of the global population.
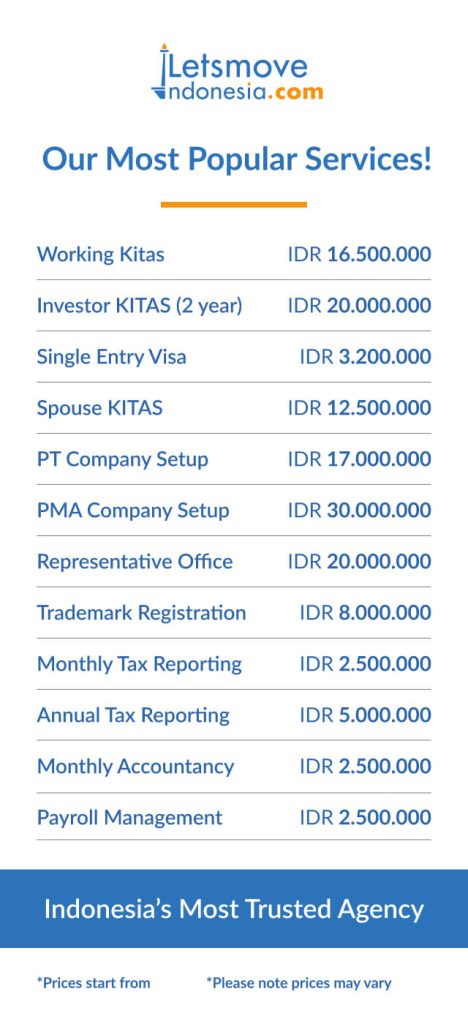
The table above shows the member countries, the year they joined BRICS, their projected GDP in 2024 (in billions of US dollars), and their estimated population in 2024 (in millions of people).
| Negara Anggota (Member Country) | Tahun Bergabung (Year Joined) | GDP 2024 (Miliar US$) (USD Billion) | Populasi 2024 (Juta Jiwa) (Millions of People) |
| Brasil (Brazil) | 2009 | 2.188 | 213 |
| Rusia (Russia) | 2009 | 2.184 | 146 |
| India | 2009 | 3.889 | 1.442 |
| China | 2009 | 18.273 | 1.409 |
| Afrika Selatan (South Africa) | 2010 | 403 | 63 |
| Mesir (Egypt) | 2024 | 380 | 107 |
| Ethiopia | 2024 | 145 | 107 |
| Iran | 2024 | 434 | 87 |
| UEA (UAE – United Arab Emirates) | 2024 | 545 | 11 |
Source: goodstats.id
Why does Indonesia join BRICS?
As one of the most economically developed countries in Southeast Asia, the addition of Indonesia is seen as a great potential for the utilisation of greater access to global markets, international investment and technological development.
Benefits of Indonesia joining BRICS
Indonesia’s potential membership in BRICS presents several significant advantages, including:
- Enhanced Economic Cooperation with Developing Nations: Closer economic ties with fellow developing economies will facilitate the expansion of Indonesia’s trade and investment networks, creating new avenues for economic growth.
- Amplified Voice in Global Governance: BRICS membership will provide Indonesia with a more prominent platform to articulate its perspectives and priorities within global decision-making processes, ensuring greater representation in international affairs.
- Strengthened Multilateral Engagement for a More Equitable Global Order: Active participation in BRICS’ multilateral initiatives will contribute to the advancement of a more just and inclusive international system.
- Expanded Market Access for Indonesian Trade and Industry: Accession to BRICS will broaden Indonesia’s international market reach, providing significant benefits to its domestic trade and industrial sectors.
- Bolstered Collaboration on Global Challenges: Enhanced cooperation within BRICS will strengthen collective efforts to address pressing global issues such as climate change, food security, and public health, fostering more effective and coordinated solutions.
Potential Disadvantages of Indonesian Membership in BRICS
While Indonesian accession to BRICS offers numerous potential benefits, certain disadvantages warrant consideration. These include:
- Increased Economic Dependence: Membership could increase Indonesia’s economic reliance on fellow BRICS members, particularly China and India. This dependence poses a risk should policy shifts or economic tensions arise within the bloc, potentially impacting Indonesia’s economic stability.
- Perception of Bias: Indonesia’s joining BRICS may lead to perceptions of preferential alignment with China and Russia, the principal architects of the group.
- Potential Constraints on Collaborative Efficacy: Divergent economic interests among BRICS nations, notably between China and India, may hinder effective cooperation within the bloc. Furthermore, economic challenges currently faced by Russia, Brazil, and South Africa could further impede the bloc’s overall stability and progress.
Enhancing Indonesia’s Export Market
Analysis from the Centre of Economic and Law Studies (CELIOS) indicates that full integration into the BRICS framework presents Indonesia with valuable new avenues for expanding its export market.
Currently, Indonesia’s export activities are largely concentrated within traditional markets, including the United States and Europe, as noted by CELIOS Economic Director Nailul Huda.
Mr. Huda explained that BRICS membership offers a strategic advantage by providing access to alternative markets and mitigating the risks associated with reliance on existing trade relationships, particularly in light of recent trade disputes with European partners.
How to navigate the export and business opportunities in Indonesia after BRICS
Indonesia’s recent inclusion in the BRICS economic bloc presents exciting new prospects for international businesses, particularly in the realm of export. However, navigating the Indonesian business landscape requires careful planning and adherence to local regulations.
Before establishing a presence in Indonesia, careful consideration of initial investment is crucial.
Key factors include:
- Market Research: Thoroughly research the Indonesian market for your specific product or service. Identify target demographics, competition, and potential demand.
- Investment Structure: Determine the most suitable investment structure, such as a foreign-owned company (PT PMA), a representative office, or a joint venture with a local partner. Each structure has different legal and tax implications.
- Capital Requirements: Understand the minimum capital requirements for establishing a foreign-owned company in Indonesia. These requirements vary depending on the business sector.
- Due Diligence: Conduct thorough due diligence on potential local partners or service providers.
Setting Up a Company in Indonesia
Establishing a legal entity is essential for conducting business in Indonesia. The most common structure for foreign investors is a PT PMA (Perseroan Terbatas Penanaman Modal Asing), a limited liability company with foreign investment.
In addition to the correct business setup, specific licenses are required for exporting from Indonesia.
Related Articles:
- Business Expansion: Top 7 Profitable Industries to Start a Business in Indonesia
- What is NIB? Why Business Identification Number Essential for PT PMAs
Streamline Indonesia Business Setup with Lets Move Indonesia
Entering the Indonesian market after the BRICS expansion offers significant opportunities, but the process of setting up a business and obtaining the necessary licenses can be challenging.
Lets Move Indonesia specialises in providing comprehensive business setup and licensing services for foreign investors in Indonesia.
We provide expert guidance on choosing the right business structure, navigating investment regulations, and preparing the necessary documentation. Our team of local specialists assist in obtaining all necessary licenses, including export licenses (API-U/API-P), ensuring compliance with Indonesian regulations.
Contact Lets Move Indonesia today for a free consultation and let us help you capitalise on the exciting export and business opportunities in Indonesia after the BRICS expansion.